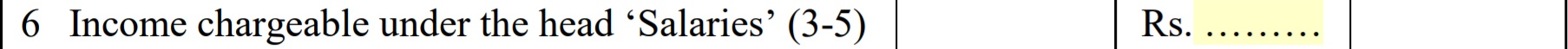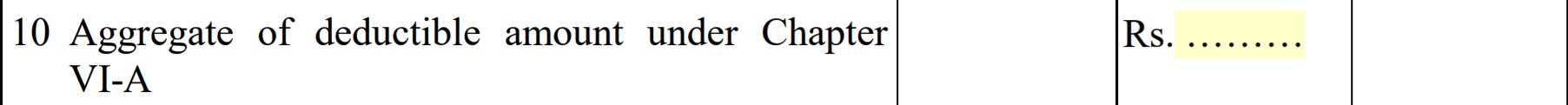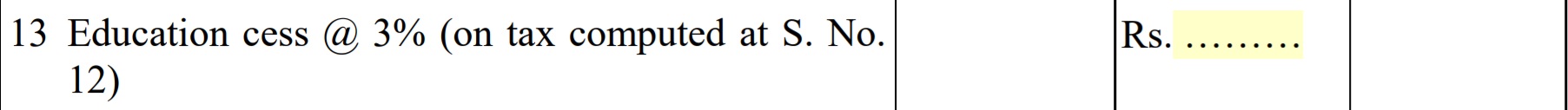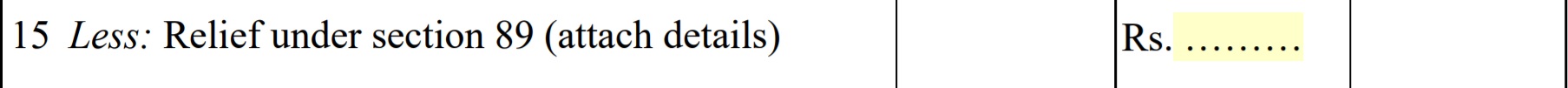Form 16 is an Income Tax form issued by the company to its salaried employees in India. It is the detailed record of the salary components and income tax deducted from the salary of the employee by the employer, during the financial year. It is mandatory for employers to issue Form 16 if he deducts TDS on salary of its employees.
Form 16 consist of two parts Part A & Part B:
Part A of Form 16
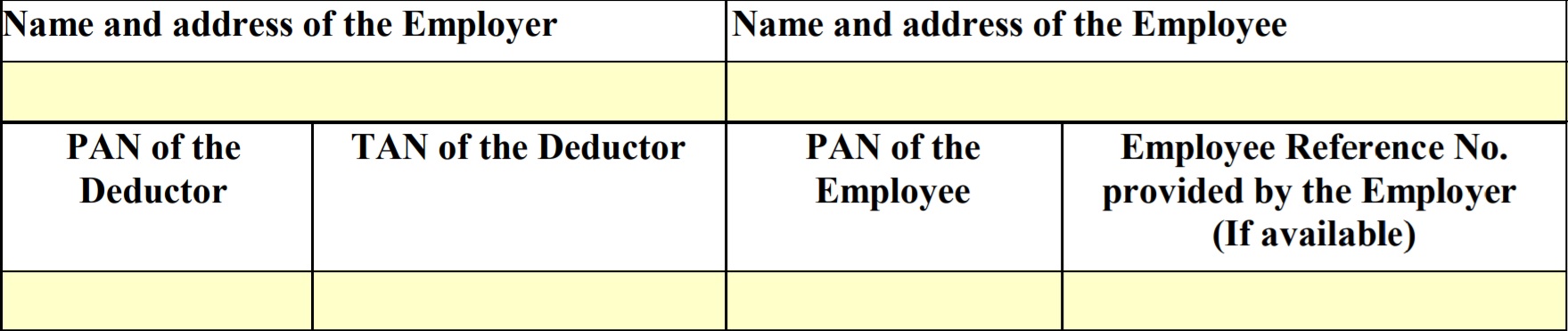
Part A contains the name & address of employer & employee with their Pan Number, TAN number (tax deduction & collection account number) of employer who is deducting the tax. Every employer who is deducting tax or collect tax on behalf of Income Tax Department is required to obtain TAN number.
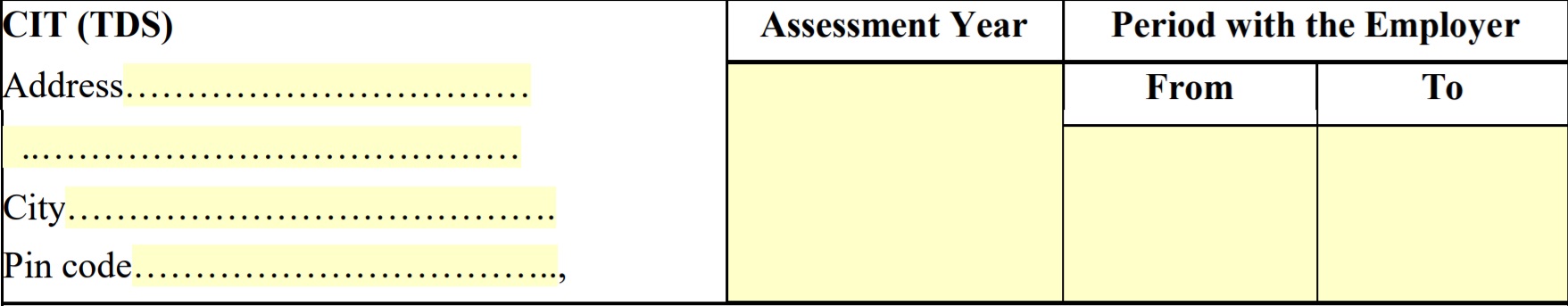
It also contains Assessment year and the period the employee spent with the employer during the Financial Year.
Assessment Year is the year in which you file your return on your income for a given financial year, means if we are filing tax today on 14.07.2018 than the assessment year (A.Y) will be 2018-19 and the financial year in which you earned the income F.Y will be 2017-18. Similarly, if we are filing tax on 14.07.2016 than A.Y will be 2016-17 and F.Y will be 2015-16 (previous year).
Part A also contains the quarter wise details of tax deducted and deposited to the government by the employer, on behalf of their employees as shown below:
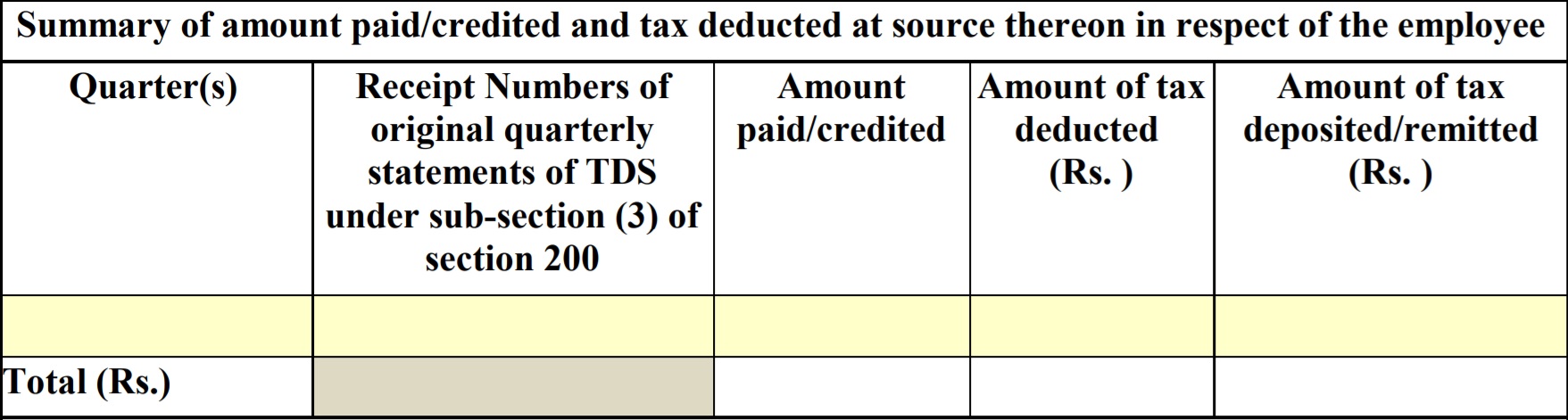
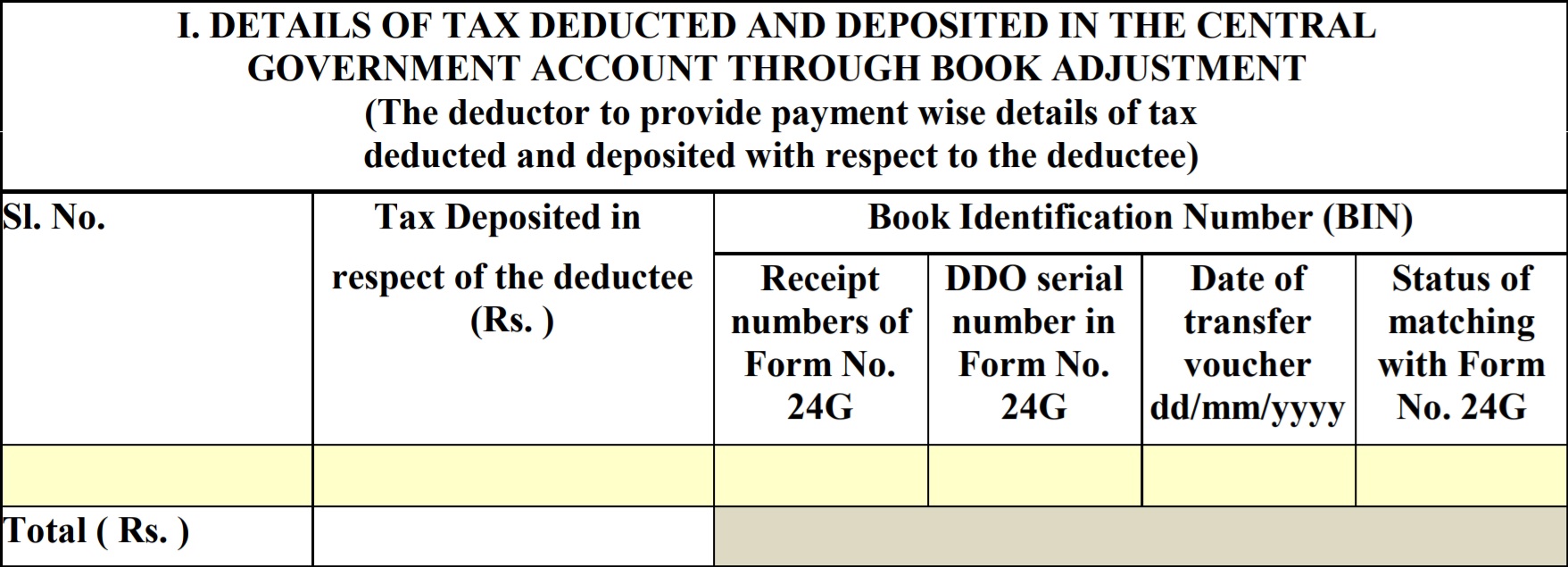
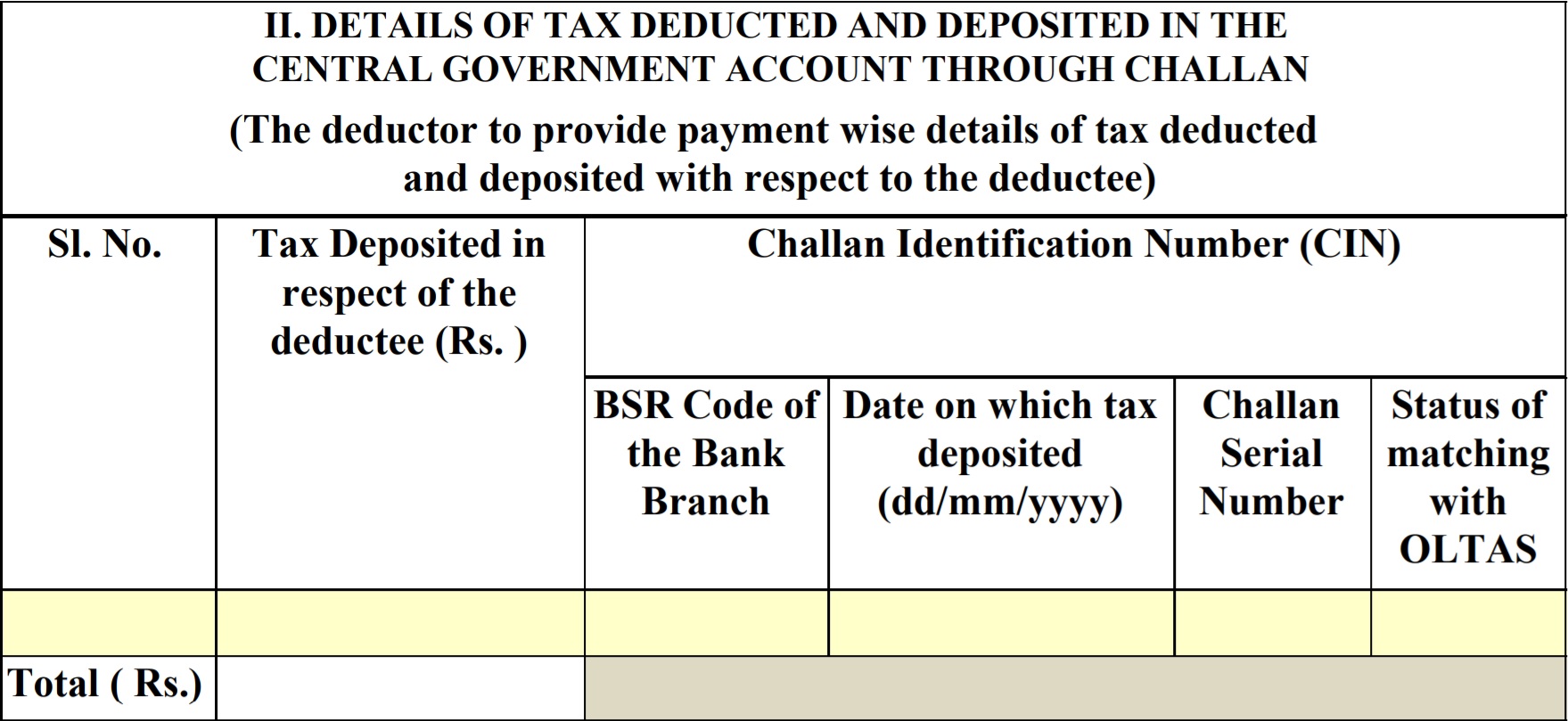
Part B of Form 16
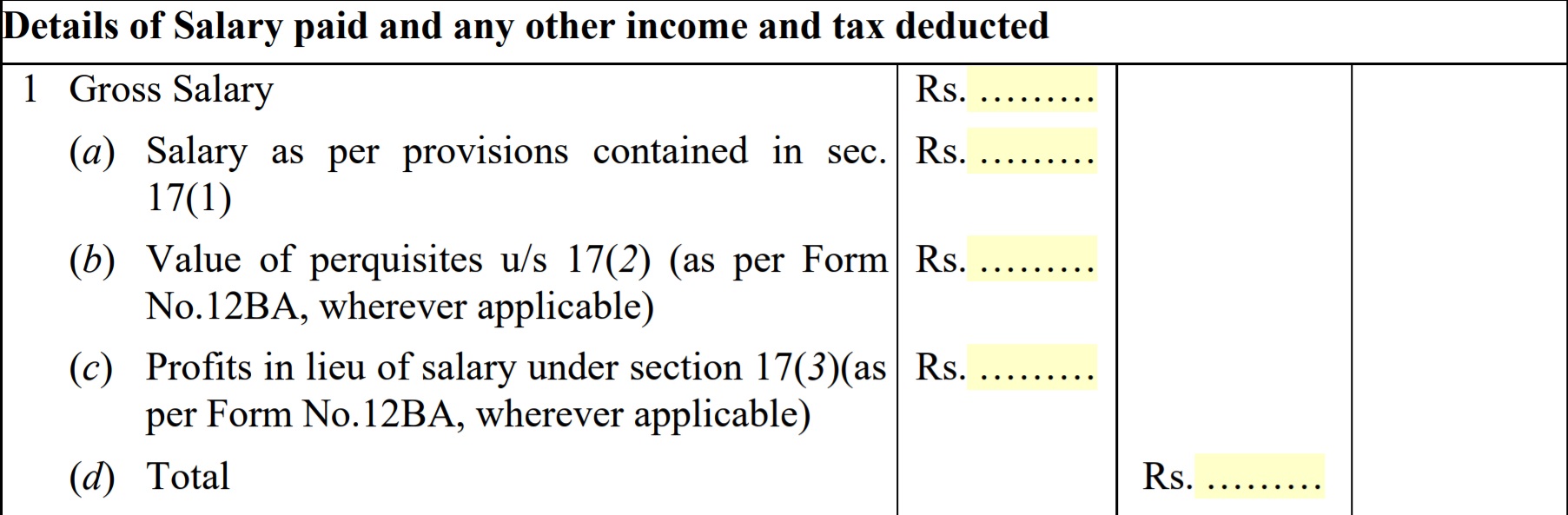
Part B consists of consolidated detail of your salary during the year. It includes breakup of your salary as well as deduction claimed by you under section 80 of the income tax act. It also shows your total taxable income and tax deducted on that income.
- Gross Salary: It is your annual salary without any deductions plus any prerequisites that you receive for example (bonus, incentives etc.)
Profit in Lieu of Salary: In lieu of means “instead of “profit in lieu of salary means any payments received by an employee from his employer in addition to salary or wages. It is taxable under the income tax act. This type of payment includes gratuity, commuted value of the pension, retrenchment benefit, interest received from provident fund or payment received by the employee before joining or after the termination of employment.
- Allowances to the extent exempt u/s 10
There are various allowances that are exempt from income tax as per section 10 for a salaried employee such as House Rent allowance, leave travel allowance, travelling allowance, academic allowance, children education allowance etc.
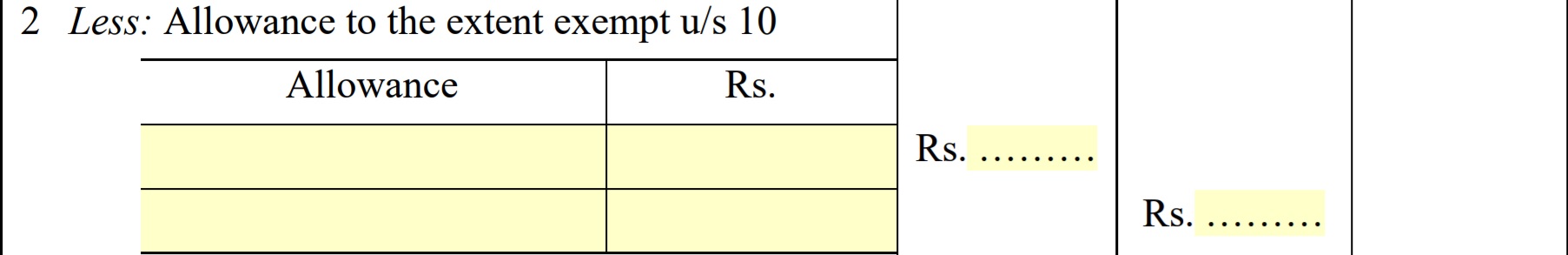
- Balance – Balance in Form 16 indicate Gross Salary minus Allowances to the extent u/s 10

4. Deduction:
- Entertainment allowance- It includes the amount of money given by the employer to their employees for meal, hotel, drink etc.
- Tax on Employment- Tax on employment or Professional tax is a tax levied by a state government. This tax is usually deducted by the employer and deposited with the state government. In income tax return, professional tax is allowed as a deduction from your salary income.

5. Aggregate of 4(a) and (b)– Is the sum total of Entertainment allowance & Tax on Employment as explained above.

6. Income chargeable under the head Salary – It provides details of the deduction allowed for Entertainment Allowance, Profession Tax or tax on Employment. It is calculated by deducting Balance obtained in point 3 minus aggregate of 4(a) and 4(b).
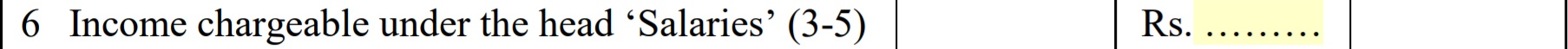
7. Details of any other income: Income from Other Sources covers income that does not fall under any of the other heads of income means incomes excluded from salary, capital gains, house property or business & profession comes under this head e.g. dividend income, income earned from winning lotteries etc.

8. Gross Total Income: Gross total income is the sum of Income chargeable under the head salary (point 6) and any other income (point 7).

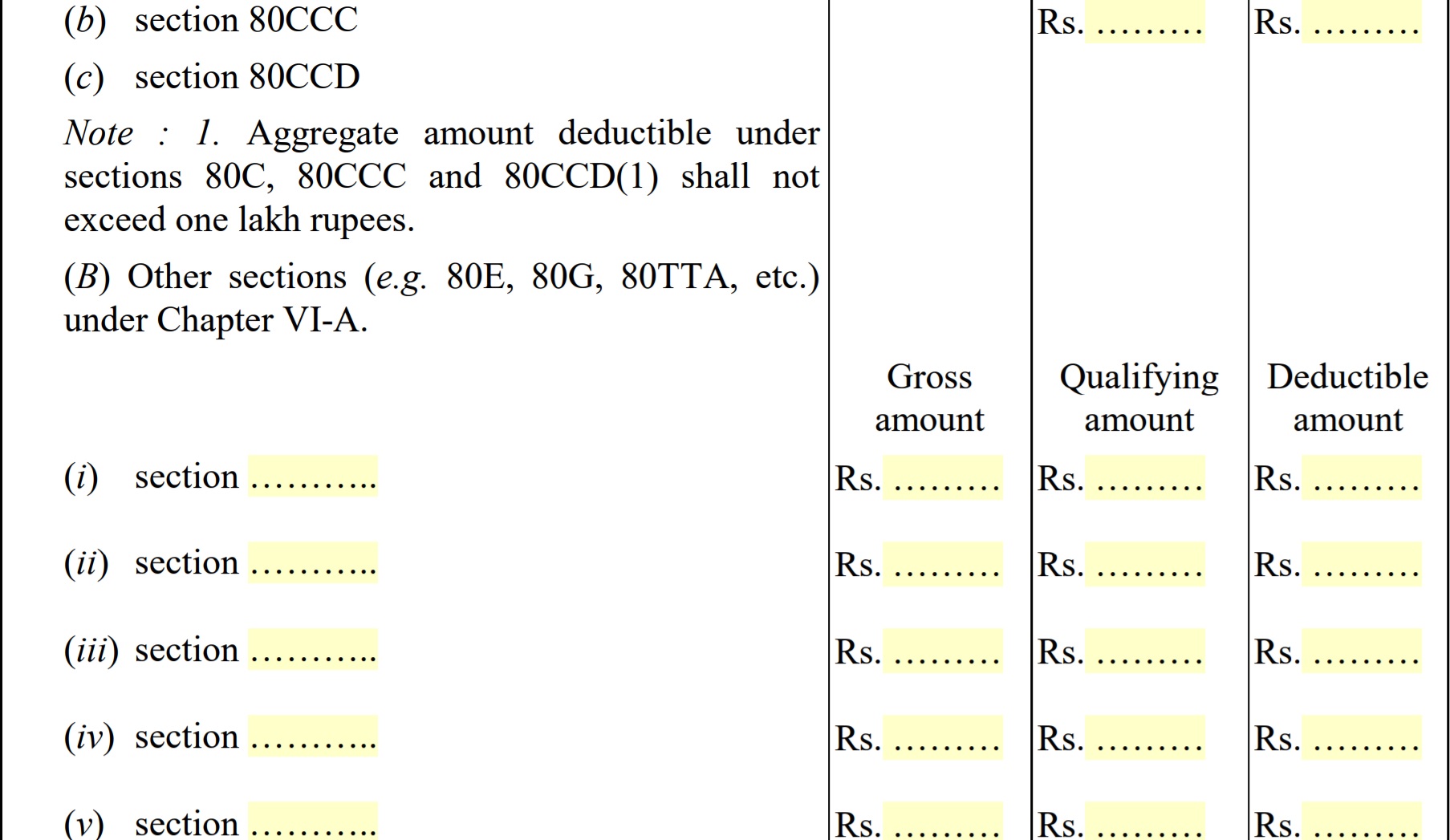
9. Deductions under Chapter VI-A(80C, 80CCC, 80CCD)
Section 80C: Under section 80C, a deduction of Rs 1, 50,000 can be claimed from your total income, if you have make payment towards life insurance, provident fund set up by government, national saving certificate, tuition fee etc. For full list please refer to section 80c of income tax act.
For full list please refer to section 80c of income tax act.
Section 80CCC: It includes a deduction for premium paid towards annuity plan of LIC or any other issuer for receiving pension from the fund. The deduction is available up to Rs 1, 50,000/-
Section 80CCD (1): It provides a deduction for individuals, who make deposits to his/her pension account. The Maximum deduction allowed is 10% of salary in case of employees and 10% of total income in case of others, up to Rs 1,50,000/-
Section 80CCD (1B): It provides a deduction up to Rs 50,000/- for contribution to the National Pension Scheme. This deduction is in addition to a maximum deduction of Rs 1, 50,000/- available under 80C, 80CCC and 80CCD(1)
Section 80CCD (2): It provides an additional deduction for the employer’s contribution to the employee’s pension account up to 10% of the salary, which means amount contributed by your employer will not be included in your taxable income, so NO INCOME TAX IS PAYABLE by you, on employer contribution amount.
Section 80D: It provides deduction up to Rs 25000/- on premium paid for medical insurance for self and family member (up to age 60 years). Deduction up to Rs 30,000/- for self & family member above 60 years
Section 80E: It provides deduction for interest on Education Loan for Higher Studies for self or family members or a relative. There is no limit on the amount that can be claimed.
Section 80G: section 80G provide tax rebate upto 100% or 50% with or without restriction for donations made to charitable organizations.
Section 80GG: Section 80GG provides a deduction in House rent paid if following conditions are met:
- The taxpayer is living on rent and not getting HRA benefit in his salary
- The taxpayer, spouse or minor child doesn’t own any residential accommodation at the place employment.
- The taxpayer doesn’t own any residential property in any other place.
Deduction available under this section is the minimum of
- Rs 60,000 annually (Rs. 5,000 monthly)
- Total rent paid minus 10% of the total income
- 25% of annual salary
Taxpayer needs to file Form 10BA with detail payment of rent to avail this deduction.
Section 80TTA: It provides a deduction up to Rs 10,000 on interest from saving account. This deduction is available to an Individual and HUF.
Section 80U: Section 80U provides tax benefits if the individual himself suffers with disability while Section 80DD offers tax benefits if an individual taxpayer’s dependent family member(s) suffers from a disability. In case of general disability means at least 40% disability, deduction of Rs 75000/- and Rs1.25 lakhs for people with severe disability (i.e., 80% or more of a disability).

- Aggregate of deductible amount under Chapter VI-A: It is total deductible amount under chapter VIA as explained above.
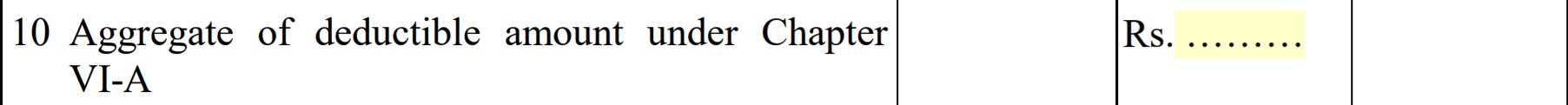
- Total Income (8-10): It is the gross total income calculated in point 8 minus total deductible amount under chapter VIA. This is the amount on which tax is calculated at the applicable tax slab.

- Tax on total income: Tax on total income will be calculated as per applicable income tax slab.

- Educational Cess: It is the tax which is levied on the tax that you have to pay i.e on your tax on total income point 12. The rate of the education cess is announced by the government at the time of budget.
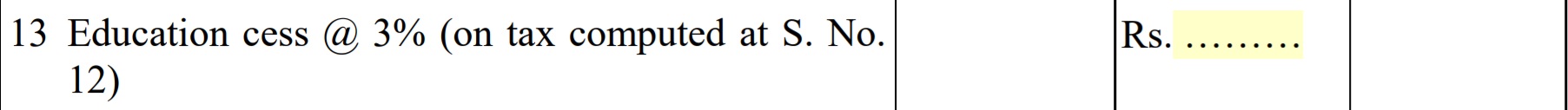
- Tax Payable: Tax payable is the sum of both taxes( tax on total Income + Educational cess)

- Relief under section 89: If you have received any portion of your salary in arrears or in advance, or your have received pension in arrears, you are allowed some tax relief under section 89. Form 10E is to be filed by the taxpayer who wants to claim relief under this section.
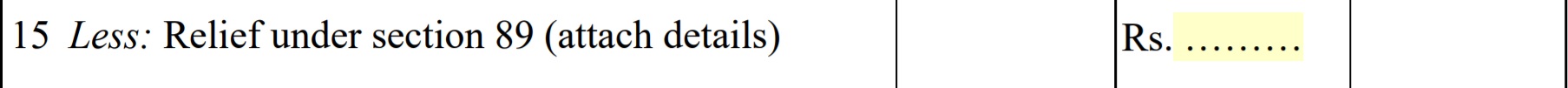
16 Tax Payable: It is calculated by deducting relief under section 89 from Tax payable (point 14).

—————-